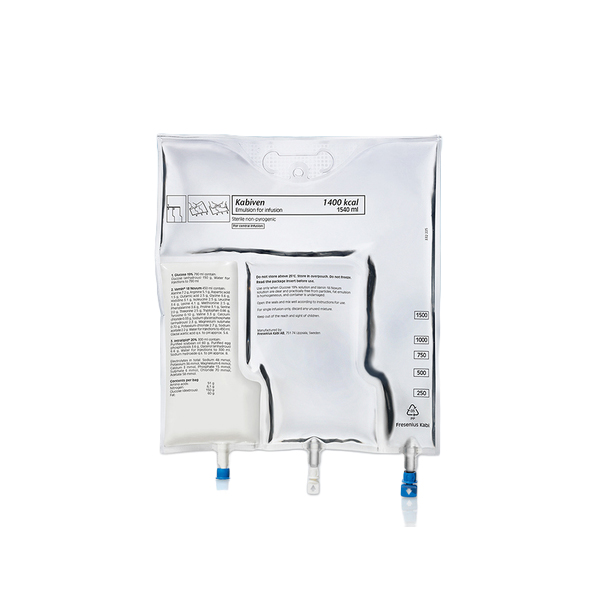
Kabiven Central
The dose should be individualised and the choice of bag size should be made with regard to the patient’s clinical condition, body weight and nutritional requirements.
Adult patients
The nitrogen requirements for maintenance of body protein mass depend on the patient’s condition (e.g. nutritional state and degree of catabolic stress). The requirements are 0.10-0.15 g nitrogen/kg body weight/day in the normal nutritional state or in conditions with mild metabolic stress. In patients with moderate to high metabolic stress with or without malnutrition, the requirements are in the range of 0.15-0.30 g nitrogen/kg body weight/day (1.0-2.0 g amino acid/kg body weight/day). The corresponding commonly accepted requirements are 2.0-6.0 g for glucose and 1.0-2.0 g for fat.
The dose range of 0.10 - 0.20 g nitrogen/kg body weight/day (0.7-1.3 g amino acid/kg body weigh/day) which covers the need of the majority of the patients. This corresponds to 19 ml - 38 ml Kabiven/kg body weight/day. For a 70-kg-patient this is equivalent to 1330 ml - 2660 ml Kabiven per day.
The total energy requirement depends on the patient’s clinical condition and is most often between 25 - 35 kcal/kg body weight/day. In obese patients the dose should be based on the estimated ideal weight.
Kabiven is produced in four sizes intended for patients with high, moderately increased, basal, or low nutritional requirements. To provide total parenteral nutrition, trace elements and vitamins should be given additionally.
Children
The ability to metabolise individual nutrients must determine the dosage.
In general the infusion for small children (2-10 years) should start with a low dose i.e. 12.5-25 ml/kg (corresponding to 0.49-0.98 g fat/kg/day, 0.41-0.83 g amino acids/kg/day and 1.2-2.4 g glucose/kg/day) and increased by 10-15 ml/kg/day up to maximum dosage of 40 ml/kg/day.
For children over 10 years of age the dosage for adults can be applied.
The use of Kabiven is not recommended in children under 2 years of age in whom the amino acid cysteine may be considered conditionally essential.
Infusion rate:
The maximum infusion rate for glucose is 0.25 g/kg/h.
Amino acid dosage should not exceed 0.1 g/kg/h.
Fat dosage should not provide more than 0.15 g/kg/h.
The infusion rate should not exceed 2.6 ml/kg body weight/hour (corresponding to 0.25 g glucose, 0.09 g amino acid and 0.1 g fat/kg body weight). The recommended infusion period is 12-24 hours.
Maximum daily dose
40 ml/kg bw/day. This is equal to one bag (largest size) to a 64 kg-patient and will provide 1.3 g amino acids/kg/day (0.21 g N/kg/day), 31 kcal/kg/day non-protein energy (3.9 g glucose/kg/day and 1.6 g fat/kg/day).
The maximum daily dose varies with the clinical condition of the patient and may even change from day to day.
Method and duration of administration
Intravenous infusion only into a central vein. Infusion may be continued for as long as required by the patient’s clinical condition.
Kabiven Peripheral
The dose should be individualised and the choice of bag size should be made with regard to the patient’s clinical condition, body weight and nutritional requirements.
Adult patients
The nitrogen requirements for maintenance of body protein mass depend on the patient’s condition (e.g. nutritional state and degree of catabolic stress).
The requirements are 0.10-0.15 g nitrogen/kg b.w./day in the normal nutritional state. In patients with moderate tohigh metabolic stress with or without malnutrition, the requirements are in the range of0.15-0.30 g nitrogen/kg b.w./day (1.0-2.0 g amino acid/kg b.w./day).
The corresponding commonly accepted requirements are 2.0-6.0 g for glucose and 1.0-2.0 g for fat.
The total energy requirement depends on the patient’s clinical condition and is oftenbetween 20-30 kcal/kg b.w./day. In obese patients the dose should be based on the estimated ideal weight.
Kabiven Peripheral is produced in three sizes intended for patients with moderately increased, basal or low nutritional requirements. To provide total parenteral nutrition, the addition of trace elements, vitamins and supplemental electrolytes may be required.
The dose range of 0.10-0.15g N/kg b.w./day (0.7-1.0 g amino acid/kg body weigh/day) and a total energy of 20-30 kcal body weight/day corresponds to approx. 27-40 ml Kabiven
Peripheral/kg b.w./day.
Children
The ability to metabolise individual nutrients must determine the dosage.
In general the infusion for small children (2-10 years) should start with a low dose i.e. 14-28 ml/kg (corresponding to 0.49-0.98 g fat/kg/day, 0.34-0.67 g amino acids/kg/day and 0.95-1.9 g glucose/kg/day) and increased by 10-15 ml/kg/day up to maximum dosage of 40 ml/kg/day.
SPC 08-337, 2008-12-19 4 (11)
For children over 10 years of age the dosage for adults can be applied.
The use of Kabiven peripheral is not recommended in children under 2 years of age in whom the amino acid cysteine may be considered conditionally essential.
Infusion rate:
The maximum infusion rate for glucose is 0.25 g/ kg b.w./h.
Amino acid dosage should not exceed 0.1 g/ kg b.w. /h.
Fat dosage should not provide more than 0.15 g/ kg b.w./h.
The infusion rate should not exceed 3.7 ml/kg b.w./h (corresponding to 0.25 g glucose, 0.09 g amino acids, 0.13 g fet per kg body weight).
The recommended infusion period for individual bags of Kabiven Peripheral is 12-24 hours.
Maximum daily dose
40 ml/kg b.w./day. This is equal to one bag (largest size) to a 64 kg-patient and will provide 0.96 g amino acids/ kg b.w./day (0.16 g N/ kg b.w./day), 25 kcal/ kg b.w./day nonprotein energy (2.7 g glucose/ kg b.w./day and 1.4 g fat/ kg b.w./day).
The maximum daily dose varies with the clinical condition of the patient and may even change from day to day.
Method and duration of administration
Intravenous infusion into a peripheral or central vein. Infusion may be continued for as long as required by the patient’s clinical condition.
In order to minimise the risk of thrombophlebitis for peripheral application, daily rotation of infusion site is recommended.